Projections of EU GDP
by Gennaro ZezzaIn our latest Strategic Analysis we estimate that a cut in the general government deficit in the United States would have strong adverse effects on unemployment and a relatively smaller impact on the U.S. public debt-to-GDP ratio, since GDP would slow down with a cut in government expenditures and transfers.
A similar strategy of deficit reduction seems to be on the agenda for many eurozone countries; notably Italy, where a new government was recently put in charge to implement unpopular tax increases that the Berlusconi government was not willing to adopt.
A comparison of our simulation for the U.S. with the European Commission’s for the eurozone may therefore be interesting.
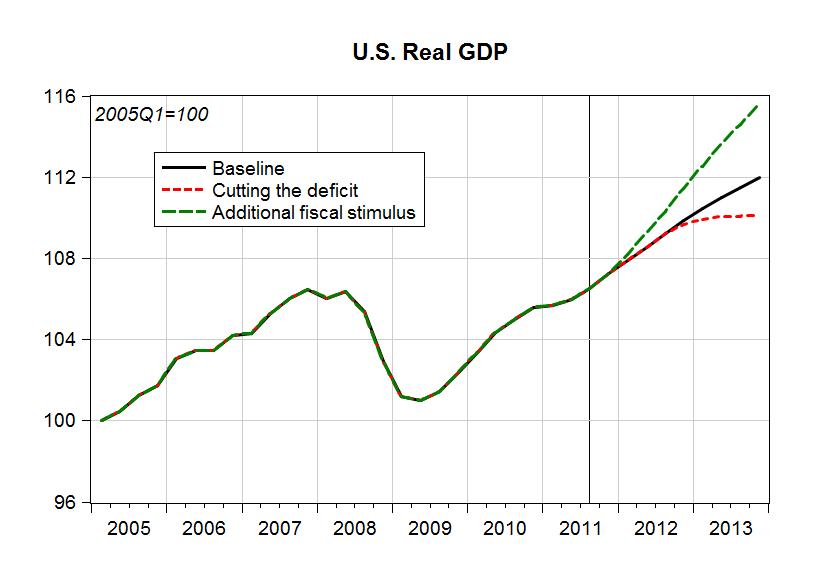
First of all, the United States is now (third quarter of 2011) back to the pre-recession level of output, as measured by real GDP. Using this figure we could say that the recession is behind us, and we can plan for the future (although this is far from true if we look at the unemployment rate!). And in our projections we show that an acceleration in aggregate demand is needed if the unemployment rate is going to be reduced (the green line), while policies to cut the government deficit will lead to stagnation (the red line) and an increase in unemployment.
Let’s look at a similar chart for Europe, taken from a simple synthesis of the new roles for economic governance in the area:
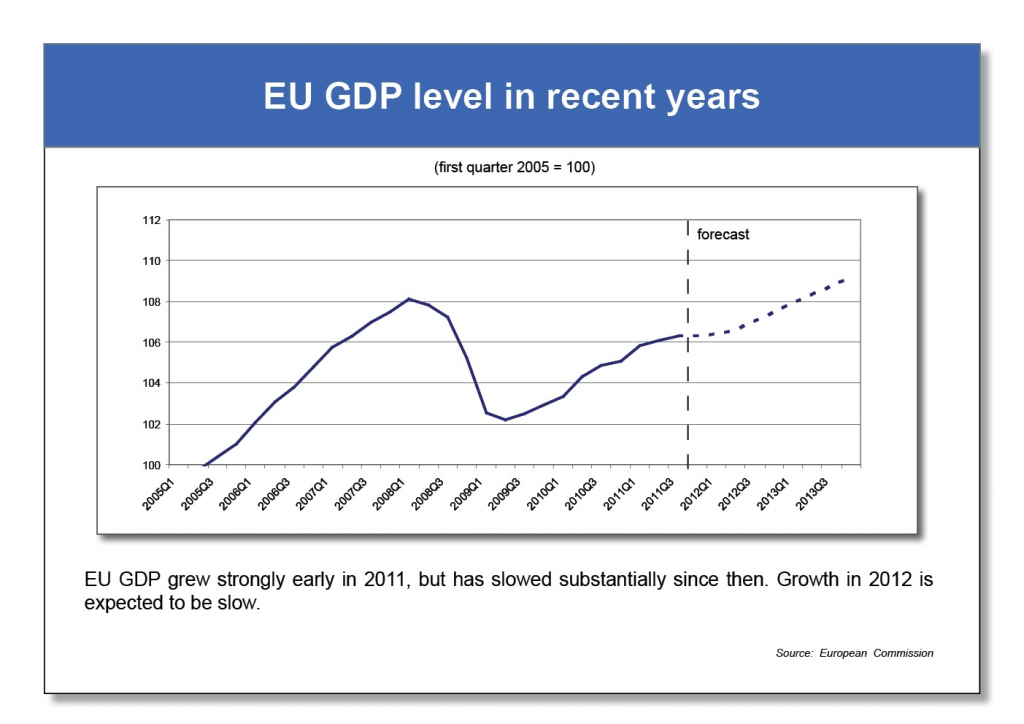
Real GDP in the area is still below its pre-recession level, and stagnating. We would think that European governments would be meeting frequently to discuss how to recover the lost ground in output and employment, but instead they meet with quite a different problem in mind: how to enforce balanced budget rules on national governments. The Italian government, still one of the largest economies in the area, is now passing a bill that will increase taxes substantially, further depressing domestic demand.
What the EU is planning is the wrong policy at the wrong time. And if the multiplier in the EU is similar to what we estimate for the United States, the consequences for the unemployment rate will be substantial.

